| Ch 2. Torsion | Multimedia Engineering Mechanics | ||||||
|
Circular Bars |
Nonuniform & Indeterminate |
Thin-walled Tubes |
Non-Circular Bars | ||||
| Circular Bars and Shafts | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Stress/Strain |
| 2. Torsion |
| 3. Beam Shr/Moment |
| 4. Beam Stresses |
| 5. Beam Deflections |
| 6. Beam-Advanced |
| 7. Stress Analysis |
| 8. Strain Analysis |
| 9. Columns |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Mechanics Eqs |
| Sections |
| Material Properties |
| Structural Shapes |
| Beam Equations |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Example |
||
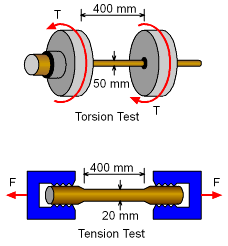 Test Specimens |
To determine mechanical properties of a material, a torsion test and a tension test was done for two different diameter bar made from the same material as shown in the figures on the left. During the torsion test, a maximum shear stress of 100 MPa was measured on a bar 50 mm diameter. The angle of twist was 2.5 degree over a length of 400 mm. The tensile test was done with a bar of 20 mm diameter and 400 mm length. The specimen had an elongation of 0.5 mm when subjected to a tensile load of 40 kN. Determine the Poisson's ratio of the material. |
|
| Solution |
||
Torsion test data: Diameter of bar, d1 = 2r1 = 50 mm Tension test data: Diameter of bar, d2 = 2r2 = 20 mm To determine the poisson's ratio, it is necessary to know the modulus of elasticity and shear modulus of the material. These can be determined using the data from the two tests. |
||
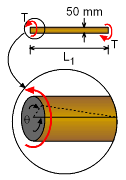 Torsion Test Details |
For the tension test Strain, Stress, Modulus of Elasticity, |
|
|
|
For the torsion test Shear Modulus, Now for Poisson's ratio, G = E / 2(1 + ν) Poisson's ratio, ν = 0.389 |
|
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Mechanics' mobile app
Includes over 500 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.