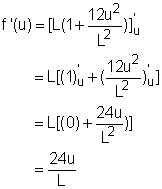| Ch 3. Derivatives II | Multimedia Engineering Math | ||||||
|
Higher Order Derivatives |
Related Rates |
Differential |
Newton's Method |
||||
| Differential | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Limits |
| 2. Derivatives I |
| 3. Derivatives II |
| 4. Mean Value |
| 5. Curve Sketching |
| 6. Integrals |
| 7. Inverse Functions |
| 8. Integration Tech. |
| 9. Integrate App. |
| 10. Parametric Eqs. |
| 11. Polar Coord. |
| 12. Series |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| MATHEMATICS - CASE STUDY SOLUTION |
||
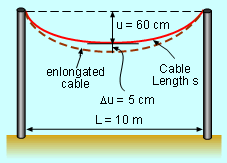 Hanging Cable |
A cable hanging between two poles forms an arc due to weight. The distance between the two poles, L, is 10 meter. The distance between the lowest point of the arc and the top of the two poles, u, is 60 cm. The mathematics formula to calculate the length of the cable, s, is In the summer, the cable goes down 5 cm. How much does the cable increase in length? Let the deflection distance and the cable's elongated length be Δu and Δs respectively. In order to find Δu, the differential of the shape function needs to be calculated. The definition of differential gives the following equation dy/dx = f '(x) Thus ds/du = f '(u) The right hand side is So In this equation, du equals to Δu and Δu = 5 cm. The lowest point is located in the middle of the two pole, which means that l = 10/2 meter = 500 cm. At this point u = 60 cm. Substitute l, u and du into the above equation gives: ds = 14.4 cm Since ds is approximately equal to Δs, so Δs
= 14.4 cm. The electric cable's length increase 14.4 cm. |
|