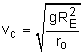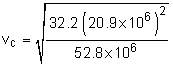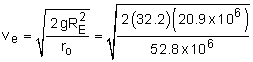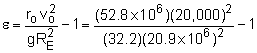| Ch 2. Particle Force and Acceleration | Multimedia Engineering Dynamics | ||||||
|
Rect. Coord. |
Normal/Tang. Coord. |
Polar Coord. |
Orbital Mechanics | Computational Mechanics | |||
| Orbital Mechanics | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| - Particle - |
| 1. General Motion |
| 2. Force & Accel. |
| 3. Energy |
| 4. Momentum |
| - Rigid Body - |
| 5. General Motion |
| 6. Force & Accel. |
| 7. Energy |
| 8. Momentum |
| 9. 3-D Motion |
| 10. Vibrations |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Dynamics Eqs |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Solution of a) |
||
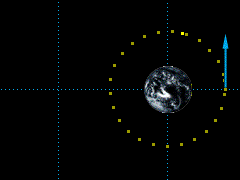 Circular Orbit, ε = 0 |
The initial velocity required to give the satellite a circular orbit can be found from, = 16,300 ft/s |
|
| Solution of b) |
||
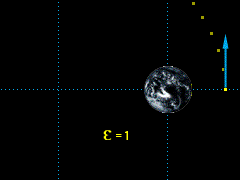 Parabolic Orbit, ε =1 |
The minimum initial velocity required to escape the earth's gravitational pull can be found from: = 23.1 x 103 ft/s |
|
| Solution of c) |
||
|
|
To find the maximum radius, the eccentricity of the orbit must be determined when the initial velocity of the satellite is 20,000 ft/sec. = 0.500 Because 0 < ε < 1, the orbit must be elliptical, and thus the maximum radius occurs at apogee. = 158 x 106 ft = 29,900 miles |
|
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Dynamics' mobile app
Includes over 400 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.