| Ch 10. Rankine Cycle | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
|
Rankine Cycle |
Reheat | Regeneration | Cogeneration | ||||
| Ideal Cogeneration Rankine Cycle | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| |
||
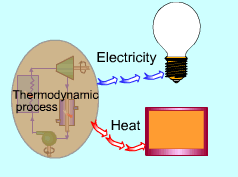
Some industries, like chemical, paper, and food processing,
require energy input in the form of heat, called
process heat. This section will introduce cogeneration power
plant, which produce process heat and electric power from the same power plant. |
||
| Cogeneration
|
||
|
|
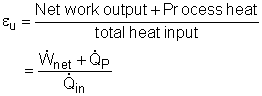
Some industries, like chemical, paper, and food processing, require input process heat. Process heat in these industries is usually supplied by steam at 5 to 7 atm and 150 to 200oC. So it is possible to have a power plant that produces electricity while meeting the process heat requirements of their industrial processes. In this way, more of the energy transferred to the fluid in the boiler is utilized for a useful purpose. In general, cogeneration is the production of more than one useful form of energy from the same energy source. Thus, this kind of power plant is called a cogeneration power plant. Either a Rankine cycle or a Brayton cycle or their combination cycle can be used as the power cycle in a cogeneration power plant. The fraction of energy that is used for either process heat or power generation is called the utilization factor of the cogeneration power plant.
|
|
| The Ideal Steam-turbine
Cogeneration
Power Plant
| ||
|
|
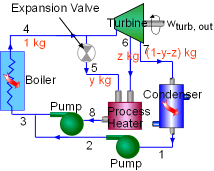
The schematic of an ideal steam-turbine cogeneration power plant is shown
on the left. Under normal operation, some steam is extracted from the turbine
at some intermediate pressure (state 6) and sent to the process heater.
The rest of the steam is expanded to the condenser pressure (state 7).
When there are high demands for process heat, all the steam can be directed to the process heater.
Also, some steam directly from the boiler can be sent to the process heater
through an expansion valve. When there is no requirement for process heat, all the steam will
expands in the turbine and the cogeneration power plant operates as an
ordinary steam power plant.
For unit mass of steam flowing through the boiler, heat and work interactions and process heat supply by a steam-turbine cogeneration power plant are: Heat Input: qin = h4 - h3 |
|
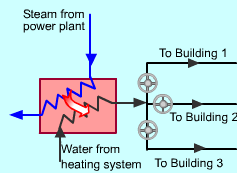 District Heating System |
One common cogeneration arrangement involves district heating. In this application a power plants is integrated into a community so that it provides electricity for industrial, commercial, and domestic use together with steam or hot water for process heat requirements. |
|