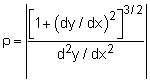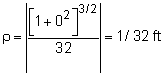| Ch 1. Particle General Motion | Multimedia Engineering Dynamics | ||||||
|
Position, Vel & Accel. |
Accel. vary w/ Time |
Accel. Constant | Rect. Coordinates | Norm/Tang. Coordinates | Polar Coordinates |
Relative Motion |
|
| Curv. Motion: Normal/Tangential | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| - Particle - |
| 1. General Motion |
| 2. Force & Accel. |
| 3. Energy |
| 4. Momentum |
| - Rigid Body - |
| 5. General Motion |
| 6. Force & Accel. |
| 7. Energy |
| 8. Momentum |
| 9. 3-D Motion |
| 10. Vibrations |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Dynamics Eqs |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
 Particle Motion along Path |
Example |
|
|
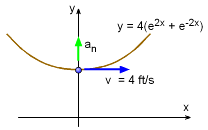
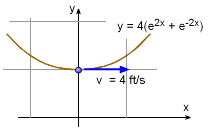
A particle moves along a wire that follows the curve y = 4(e2x + e-2x) at a constant velocity of 4 m/s. What is the normal acceleration of the particle when x = 0?
|
||
| Solution |
||
|
|
Since the velocity is constant, there is no acceleration tangent to its path. However, there is acceleration normal (perpendicular) to the path as given by, an = v2/ρ Need to determine, ρ dy/dx = d[ 4(e2x + e-2x) ] / dx d2y/dx2 = d[ 8(e2x - e-2x ) ] / dx (dy/dx)x=0 = 8(1 - 1) = 0 Substituting back into the acceleration equation, an = 512 ft/s2 |
|
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Dynamics' mobile app
Includes over 400 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.