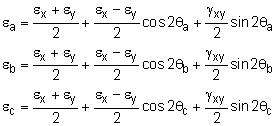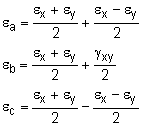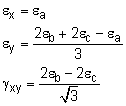| Ch 8. Strain Analysis | Multimedia Engineering Mechanics | ||||||
|
Plane Strain |
Mohr's Circle for Strain |
Strain Gages |
|||||
| Strain Gages and Strain Rosette | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Stress/Strain |
| 2. Torsion |
| 3. Beam Shr/Moment |
| 4. Beam Stresses |
| 5. Beam Deflections |
| 6. Beam-Advanced |
| 7. Stress Analysis |
| 8. Strain Analysis |
| 9. Columns |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Mechanics Eqs |
| Sections |
| Material Properties |
| Structural Shapes |
| Beam Equations |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Strain Gage Basics |
||
|
|
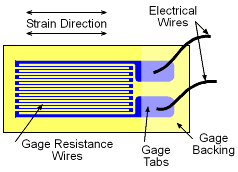
It is not possible (currently) to measure stress directly in a structure. However, it is possible to measure strain since it is based on displacement. There are a number of techniques to measure strain but the two more common are extensometers (monitors the distance between two points) and strain gages. Strain gages are constructed from a single wire that is wound back and forth. The gage is attached to the surface of an object with wires in the direction where the strain is to be measured. The electrical resistance in the wires change when they are elongated. Thus, the voltage change in the wires can be collaborated to the change in strain. Most strain gage measurement devices automatically collaborate the voltage change to the strain, so the device output is the actual strain. |
|
| Strain Rosette |
||
|
|
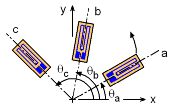
Since a single gage can only measure the strain in only a single direction, two gages are needed to determine strain in the εx and εy. However, there is no gage that is capable of measuring shear strain. There is a clever solution to finding shear strain. Three gages are attached to the object in any three different angles. Recall, any rotated normal strain is a function of the coordinate strains, εx, εy and γxy, which are unknown in this case. Thus, if three different gages are all rotated, that will give three equations, with three unknowns, εx, εy and γxy. These equations are, Any three gages used together at one location on a stressed object is called a strain rosette. |
|
| Strain Rosette - 45o |
||
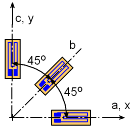 Strain Gage Rosette at 45o |
To increase the accuracy of a strain rosette, large angles are used. A common rosette of three gages is where the gages are separated by 45o, or θa = 0o, or θb = 45o, or θc = 90o. The three equations can then be simplify to Solving for εx, εy and γxy gives, |
|
| Strain Rosette - 60o |
||
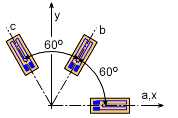 Strain Gage Rosette at 60o |
Similarly, if the angles between the gages are 60o, or θa = 0o, or θb = 60o, or θc = 120o., the unknown strains, for εx, εy and γxy will be, |
|
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Mechanics' mobile app
Includes over 500 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.