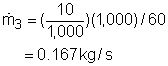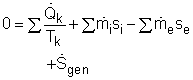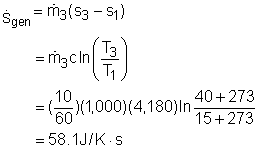| Ch 6. Entropy | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
| Entropy | Tds Relations |
Entropy Change |
Isentropic Process |
Isentropic Efficiency |
Entropy Balance (1) |
Entropy Balance (2) |
Reversible Work |
| Entropy Balance for Control Volume | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
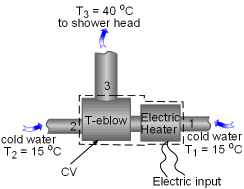
The entropy generated when Austin's father takes his daily shower needs to be determined. Assumptions:
|
||
|
|
Take the T-elbow and the electric heater together as a control volume shown on the left. Cold water at 15oC enters the electric heater (denoted as 1) and the T-elbow (denoted as 2), and leaves the T-elbow at 40oC. Since the flow is steady, the mass balance for this control volume is The mass flow rate to the shower head is |
|
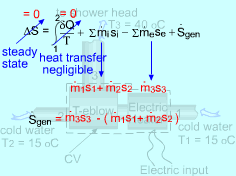 Simplify the Entropy Balance of the Control Volume |
The entropy balance for a control volume at steady state is It is assumed that there is no heat transfer between the pipes and the surroundings. That means no entropy flows in or out of the control volume associated with the heat transfer. The control volume has electric work input, but the work is entropy free. Hence, the entropy balance for this steady-flow control volume can be simplified as Since water enters the T-elbow and the electric heater at the same temperature, s1 = s2 Also, with the mass balance, the entropy generation can be determined by Hence, a 15-minute shower will generate entropy Sgen = (15)(60)(58.1) = 52,290 J/K = 52.3 kJ/K |
|