| Ch 7. Stress Analysis | Multimedia Engineering Mechanics | ||||||
|
Plane Stress |
Principal Stresses |
Mohr's Circle for Stress |
Failure |
Pressure Vessels |
|||
| Pressure Vessels | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Stress/Strain |
| 2. Torsion |
| 3. Beam Shr/Moment |
| 4. Beam Stresses |
| 5. Beam Deflections |
| 6. Beam-Advanced |
| 7. Stress Analysis |
| 8. Strain Analysis |
| 9. Columns |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Mechanics Eqs |
| Sections |
| Material Properties |
| Structural Shapes |
| Beam Equations |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Example |
||
|
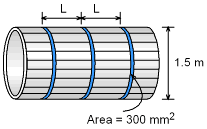
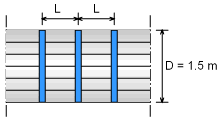
A penstock for a hydro power plant has an inside diameter of 1.5 m and is composed of wooden staves bound together by steel hoops. The cross-sectional area for each steel hoop is 300 mm2. If the allowable tensile stress for the steel is 130 MPa, what is the maximum space, L, between the hoop bands under a head of water of 30 m? The mass density of water is 1,000 kg/m3. The water pressure can be assumed to be the same at all interior locations of the penstock. |
|
| Solution |
||
|
The pressure corresponding to a head of 30 m water is given by Circumferential stress in the steel bands is considered as the failure criteria for a safe design. If the maximum spacing between hoops is denoted as L, then each hoop must resist the water pressure over a length L of the penstock. |
|
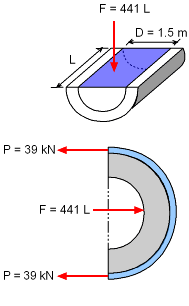 Direct Evaluation of Bursting Force F |
The bursting force F, acting over the flat surface of the fluid equals the pressure intensity p multiplied by the area, DL, over which it acts. L = 0.1769 m = 177 mm |
|
| Comments |
||
| Please note, this example is a simplistic presentation of an actual penstock. An engineer in Argentina, Rodrigo Salvioli, who worked on real hydro power plant penstocks, correctly mentioned that,
|
||
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Mechanics' mobile app
Includes over 500 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.