| Ch 2. Fluid Statics | Multimedia Engineering Fluids | ||||||
|
Pressure Variation |
Pressure Measurement |
Hydrostatic Force(Plane) |
Hydrostatic Force(Curved) |
Buoyancy | |||
| Hydrostatic Force -Curved Surface | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Fluid Statics |
| 3. Kinematics |
| 4. Laws (Integral) |
| 5. Laws (Diff.) |
| 6. Modeling/Similitude |
| 7. Inviscid |
| 8. Viscous |
| 9. External Flow |
| 10. Open-Channel |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Fluid Eqs |
| Water/Air Tables |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Questions |
||
|
|
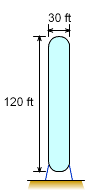
One type of water tank for a municipal water
supply system is a standpipe. If the standpipe is 120 ft tall and the
diameter is 30 ft, calculate the stress in the 0.5 in. thick steel plates
at the bottom of the tank. Assume both ends are spherical and the tank is completely filled with water. Ignore minor pressure variations in curved ends. |
|
| Solution |
||
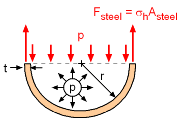
The dimensions of the standpipe are: Water pressure (hydrostatic pressure variation) at the bottom of the standpipe p = γw z = (62.4 pcf)(120 ft) From the free body diagram, for equilibrium Fs = pA The hoop stress is calculated as σh = pr / 2t = (52 psi)(15 ft)(12 in/ft) / [2 (0.5 in)] Note 1: the tensile strength of steel is on the order of 40 - 80 ksi, so 0.5 in. is sufficient thickness. Note 2: final plate thickness used in design must consider wind and/or earthquake loads. |
||
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Fluids' mobile app
Includes over 250 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.