| Ch 1. Basics | Multimedia Engineering Fluids | ||||||
|
Mass Density |
Ideal Gas Law |
Viscosity |
Surface Tension |
Vapor Pressure |
|||
| Surface Tension | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Fluid Statics |
| 3. Kinematics |
| 4. Laws (Integral) |
| 5. Laws (Diff.) |
| 6. Modeling/Similitude |
| 7. Inviscid |
| 8. Viscous |
| 9. External Flow |
| 10. Open-Channel |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Fluid Eqs |
| Water/Air Tables |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
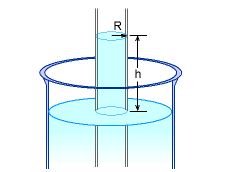 Capillary Action |
The height of the water column is given as a function of the contact angle (θ), radius of the tube (R), density (ρ) and surface tension (σ) of the liquid as follows: h = 2σcosθ / ρgR For water in contact with a clean glass, the contact angle is zero, hence the equation reduces to h = 2σ / ρgR For water at 30oC, the surface tension and density are 0.0712 N/m and 995.7 kg/m3 respectively, as noted in the theory page. For a tube with a radius of 1 mm: h = 2(0.0712)(106)/(995.7)(9.8)(1)
For a tube with a radius of 10 mm: h = 2(0.0712)(106)/(995.7)(9.8)(10)
Note that the water rise in the capillary tube decreases with an increase of the radius of the tube. |
|
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Fluids' mobile app
Includes over 250 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.