| Ch 7. Rigid Body Energy Methods | Multimedia Engineering Dynamics | ||||||
| Rot. Work & Energy | Conservation of Energy | ||||||
| Conservation of Energy | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| - Particle - |
| 1. General Motion |
| 2. Force & Accel. |
| 3. Energy |
| 4. Momentum |
| - Rigid Body - |
| 5. General Motion |
| 6. Force & Accel. |
| 7. Energy |
| 8. Momentum |
| 9. 3-D Motion |
| 10. Vibrations |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Dynamics Eqs |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
|||||
|
If all the forces acting on a system, such as gravity or spring forces, are conservative, the Principle of Work and Energy can be written as This equation is referred to as the Principle of Conservation of Energy. This relationship is true since the work of a conservative force is independent of its path. Frictional forces are not conservative forces since energy is lost to frictional heat. Work on a rigid body is the same as work on a particle, with the addition of rotational energy. |
|||||
| Potential Energy - Gravity |
|||||
|
|
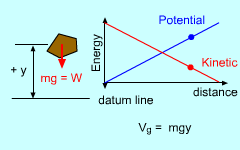
Gravity is a conservative force and thus the amount of work needed to move an object through the gravitational field is the same regardless of the path. Gravitational potential energy is directly related to how high the object is above a given reference plane (called a datum line), Vg = mgy Objects below the datum line require additional work to raise them up to the datum line. Thus those objects have negative potential energy. |
||||
| Potential Energy - Spring or Elastic |
|||||
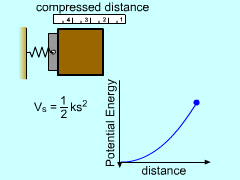 Spring Potential Energy |
A compressed or stretched spring has stored energy that will produce work if released. This energy is called elastic potential energy and is modeled as Vs = 1/2 k s2 |
||||
| Kinetic Energy - Rigid Body |
|||||
|
Recall from the Rotational Kinetic Energy and Work section section, kinetic energy for a rigid body is T = 1/2 m vG2 + 1/2 IG ω2 Here, VG is the linear velocity and ω is the angular velocity about the body's center of gravity G. |
|||||
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Dynamics' mobile app
Includes over 400 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.