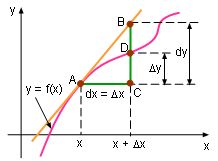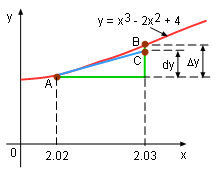| Ch 3. Derivatives II | Multimedia Engineering Math | ||||||
|
Higher Order Derivatives |
Related Rates |
Differential |
Newton's Method |
||||
| Differential | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Limits |
| 2. Derivatives I |
| 3. Derivatives II |
| 4. Mean Value |
| 5. Curve Sketching |
| 6. Integrals |
| 7. Inverse Functions |
| 8. Integration Tech. |
| 9. Integrate App. |
| 10. Parametric Eqs. |
| 11. Polar Coord. |
| 12. Series |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Search |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| Author(s): |
| Hengzhong Wen |
| Chean Chin Ngo |
| Meirong Huang |
| Kurt Gramoll |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| |
||
The notation of dy/dx has been regarded as a single symbol for a derivative in previous sections. It looks like a fraction but is not one. In this section, dy and dx, named differential, are given a meaning so that their quotient is the derivative of the function. |
||
| Differential |
||
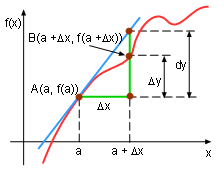
| Let y = f(x) and is differentiable. If the differential dx is an independent variable, then the differential dy is defined in terms of dx as dy = f '(x)dx. Thus dy/dx = f '(x) |
||
|
||
| Geometric Meaning of Differential |
||
|
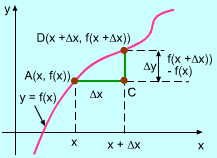
Let A(x, f(x)) and D((x + Δx), f(x + Δx)) be points on function y. Let dx = Δx. Then the change Δy equals f(x + Δx) - f(x). |
|
|
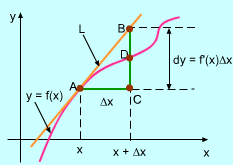
The slope of the tangent line AB is the derivative of function y, that is In this equation dy is the amount of changes in y axis along the tangent line to the curve at point A, and dx is the changes in x axis which is Δx. The definition of derivative gives therefore, that is when Δx approaches 0. In this equation dx = Δx, so therefore, dy ≈ Δy. |
|
| Linear Approximation
|
||
|
|
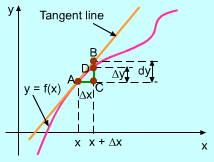
Differential can calculate the approximate value of another poiont nearby. In the diagram, the coordinate of point B is (a + Δx, f(a + Δx)). The value of its y coordinate is f(a + Δx) = f(a) + Δy When Δx is small dy ≈ Δy and f(a + Δx) ≈ f(a) + dy . This formula is commonly used to calculate approximate values of functions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
This concept can be understood by calculating the the value of Δy and dy when the value of x changes from 2.02 to 2.03 for the function of y = x3 - 2x2 + 4. Substitute a = 2.02 into y = y = x3 - 2x2 + 4, f(a) = f(2.02) = 2.023 - 2(2.02)2 + 4 = 4.081608 so point A(2.02, 4.081608) f(a) = f(2.03) = 2.033 - 2(2.03)2 + 4 = 4.123627 This gives point B(2.03, 4.123627) Δy = f(2.03) - f(2.02) = 4.123627 - 4.081608 = 0.042019 The derivative of y is y ' = (x3 - 2x2 + 4) ' = 3x2 - 6 According to differential definition, dy = y 'dx = (3x2 - 6)dx In this example, dx = Δx = 2.03 -2.02 = 0.01. Substituting dx = 0.01 and x = 2.02 into equation dy gives dy = (3x2 - 6)dx = (3(2.02)2-6)(0.01) = 0.062412 Notice that Δy and dy are very close in this case.The formula f(a + Δx) ≈ f(a) + dy or f(a + Δx) ≈ f(a) + f '(x-a) is called the linear approximation of the function at point a. |
|