| Ch 1. Basics | Multimedia Engineering Statics | ||||||
| Problem Solving | Units | ||||||
| Units | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Vectors |
| 3. Forces |
| 4. Moments |
| 5. Rigid Bodies |
| 6. Structures |
| 7. Centroids/Inertia |
| 8. Internal Loads |
| 9. Friction |
| 10. Work & Energy |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systems of Units, S.I. and U.S. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
There are two widely used systems of units: the International System (or Systeme International d'Unites in French), S.I.; and the U.S. System, U.S. The base units in the S.I. system are meters (m) for length, seconds (s) for time, and kilograms (kg) for mass. The force unit is derived using Newton's 2nd Law: F = ma = 1 kg (1 m/s2) = 1 kg m/s2 = 1 N The base units in the U.S. system are feet (ft) for length, seconds (s) for time, and pounds (lb) for force. The mass unit is derived using Newton's 2nd Law: m = F/a = 1 lb/(ft/s2) = 1 lb s2/ft = 1 slug The base units are compared in the table the left. These units are used in 90% of all Statics problems, and other units PSI (pounds per square inch) are just combinations of the basic four units. It is important to remember, however, that only three of the four units are independent. The fourth one is derived from the other three.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion Ratios |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conversion ratios relate one set of units to another set and are commonly used to quickly convert between units. Some basic ratios are shown at the left. The Units Appendix has a large selection of conversion ratios for both SI and US units. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Converting Between Units |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
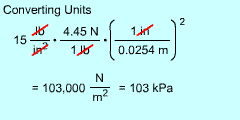 Converting Units |
When converting between the different systems of units, use the conversion factors to eliminate the unwanted unit. All units will cancel if the correct conversion ratios are used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||