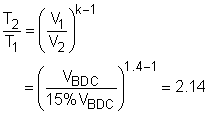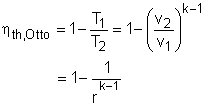| Ch 8. Gas Power Cycle | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
|
Otto Cycle |
Diesel Cycle |
||||||
| Otto Cycle | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
In Max's senior capstone design, they need to determine the power generated and the thermal efficiency of the prototype engine supplied by the Handa Car Company. Assumptions:
|
||
|
|
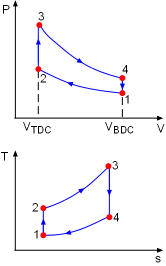
The P-v and T-s diagrams of an ideal Otto cycle are shown on the left. The working fluid contained in the cylinder of the car engine forms a closed system. (1) Determine the power generated by this four-stroke-four-cylinder spark-ignition (SI) engine In an Otto cycle, process 1-2 is an isentropic compression process. According to the data given, temperature and pressure at state 1 are T1 = 15oC Also, the T-s diagram shows the temperature of the air reaches its maximum value at state 3. That is, T3 = 1800oC In the four processes of the Otto cycle, only processes 1-2 and 3-4 have work interaction. The energy balance in these two processes are, -w12 = u2 - u1 -w34 = u4 - u3 The net work output is the sum of the work at process 1-2 and process 3-4. wnet = w12 +
w34 =
(u1 - u2) +
(u3 - u4) The cold-air-standard assumption states that the working fluid is air and modeled as an ideal gas, and all the processes are reversible. Hence, the relation between state 1 and 2 is T2 can be determined from the above relation. T2 = 2.14T1 = 2.14(15 + 273) = 616.3 K = 343.3oC Since v1 = v4 and v2 = v3, and process 3-4 is an isentropic process, T3 is given as 1800oC. Substitute T1, T2, and T3 to the above equation gives T4. T4 = (288/616.3)(1800
+ 273) Substitute all the data to the expression of the net work gives, wnet = cv12(T1 - T2) +
cv34(T3 -
T4) |
|
The mass of the air in the cylinder can be determined by the properties at state 1. First, the displacement volume is given as Vdis = 1 L = 0.001 m3 Using the relation between the volume at the bottom dead center (BDC), volume at the top dead center (TBC) and the displacement volume, the volume at the BDC, which equals V1 can be determined as VBDC = VTBC + Vdis = 15%VBDC + Vdis V1= VBDC = Vdis/85% = 0.00117 m3 At 15oC and 100 kPa, the density of air is 1.2 kg/m3. The mass of the air in the cylinder is m = 1.2(0.00117) = 0.0014 kg The total net work of one cylinder is Wnet,one = 0.0014(557.2) = 0.78 kJ The total power of four cylinders is Wnet = 4(0.78) = 3.12 kJ The piston of a four-stroke engine executes four strokes within the cylinder when the crankshaft completes two revolutions for each thermodynamic cycle. The crankshaft rotates at 2600 RPM. Thus, there is 1300 thermodynamic cycles per minute. Wnet, total = (3.12)(1300)/60 = 67.6 kW |
||
(2) Determine the thermal efficiency of the SI engine The thermal efficiency for an Otto cycle is defined as The compression rate is defined as the ratio of the volume of the air when the piston reaches its bottom dead center (BDC) to the volume of air when the piston reaches its top dead center (TDC). r =VBDC/VTDC = VBDC/(15% VBDC) = 6.7 Substitute r into the thermal efficiency expression gives, |
||