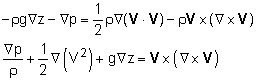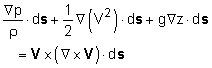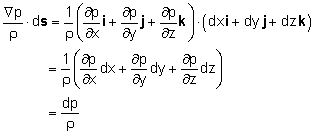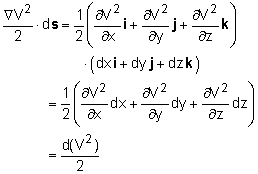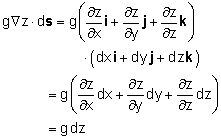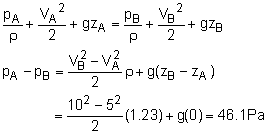| Ch 5. Fundamental Laws (Differential) | Multimedia Engineering Fluids | ||||||
|
Conservation Mass |
Navier-Stokes and Euler's |
Conservation Energy |
|||||
| Navier-Stokes & Euler's Equations | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Fluid Statics |
| 3. Kinematics |
| 4. Laws (Integral) |
| 5. Laws (Diff.) |
| 6. Modeling/Similitude |
| 7. Inviscid |
| 8. Viscous |
| 9. External Flow |
| 10. Open-Channel |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Fluid Eqs |
| Water/Air Tables |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
|
(a) For steady flow, Euler's equation in vector form is given by: Now substitute the vector identity to write Euler's equation as |
|
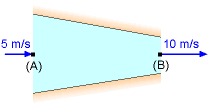
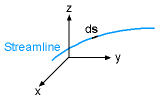 Differential Length on a Streamline |
In order to obtain Bernoulli's equation, one needs to integrate the above equation along a streamline. Hence, take the dot product of Euler's equation with a differential length ds along the streamline as follows: Recognize that the differential length ds can be expressed in terms of the Cartesian coordinates as ds = dx i + dy j + dz k Each term on the left hand side of Euler's equation can be evaluated as follows:
Since streamlines are constructed such that they are tangent to the velocity
field, the differential length ds is parallel to the velocity V.
The vector Euler's equation thus becomes which can be readily integrated to yield For constant density, the above equation reduces to the famous Bernoulli's equation |
|
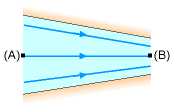 Streamline between Point A and B |
(b) Apply Bernoulli's equation between the inlet and outlet of the nozzle (i.e., along the streamline between points A and B), |
|
Practice Homework and Test problems now available in the 'Eng Fluids' mobile app
Includes over 250 free problems with complete detailed solutions.
Available at the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.