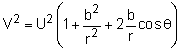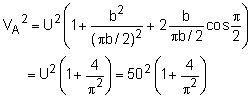| Ch 7. Incompressible and Inviscid Flow | Multimedia Engineering Fluids | ||||||
|
Bernoulli's Equation |
Flow Measurements |
Superposition of Flows |
Flow around Cylinder |
||||
| Superposition of Flows | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Fluid Statics |
| 3. Kinematics |
| 4. Laws (Integral) |
| 5. Laws (Diff.) |
| 6. Modeling/Similitude |
| 7. Inviscid |
| 8. Viscous |
| 9. External Flow |
| 10. Open-Channel |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Fluid Eqs |
| Water/Air Tables |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
|
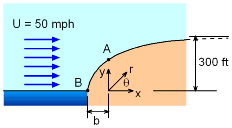
The present problem is solved using the potential flow past a half-body. As shown in the theory section, the magnitude of the velocity at any point is given by To determine the actual wind speed at any point along the surface, variables b, r and θ need to be determined. Note that b is the distance between the source and the stagnation point (see theory section). The stagnation point (i.e., point B) is given by θ = π and rstagnation = b = m/2π U and the stream function at this point is ψstagnation = πbU The stream function that passes through the stagnation point and along the hill, is then obtained as ψ = πbU = U r sinθ + b U θ which can be rearranged to give r = b(π - θ)/sinθ or y = b(π - θ) |
|
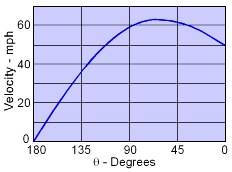 Velocity Variation on Half-body Surface |
The above expression gives the radius location along the hill. Note that as θ approaches 0 (i.e., towards inland), y approaches πb. For this problem, πb becomes 300 ft. Thus, b equals 300/π. At the proposed site (i.e., point A), θA is π/2, and the radius (rA) is determined to be πb/2. The velocity at point A is then calculated as VA = 59.27 mph The velocity for all angles is given at the left. Notice, the velocity is zero at the front stagnation point, and rises to a maximum at about 120 degrees. the downstream final velocity will be the same as the initial velocity, 50 mph. |
|