| Ch 2. Pure Substances | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
| Phase |
Property Diagrams |
Property Tables |
Ideal Gas |
||||
| Ideal Gas | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
While the hot air balloon is still in the air. The mass of the hot air and the average temperature in the balloon needs to be determined. Assumptions: The air is ideal gas with gas constant R = 287 J/(kg-K). (1) The mass of air in the balloon Since the air in the balloon is ideal gas, it obeys the ideal-gas equation of state. PV = mairRT where |
||
|
|
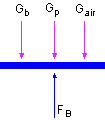
Since the balloon is open to the air, the pressure P in the balloon is the same as the ambient pressure. According to the force diagram shown on the left, the sum of all forces should be zero when the balloon is still in the air. FB - (Gb + Gp + Gair) = 0 FB = ρcool airgVballoon = ρcool airgπ (4/3)(D/2)3 ρcool air = P/(RT) Rearranging the equation to give the expression of mass of the hot air. mair = FB/g - mb - 3(mp) With all the data known mair = (1.089)(9.8)(4/3)π(10)3 /9.8
- 80 -
3(65) (2) The average temperature in the balloon After the mass of hot air is determined, the average temperature of the hot air can be determined using the ideal-gas equation of state. PV = mairRT (3) The movement of the balloon if the local air temperature is 30 oC The density of the air decreases with the temperature increases. Hence the buoyancy force will decrease and the balloon will move downward. Repeating the solution above, the temperature of the hot air equals 50.38 oC if the balloon keeps still again. |
|