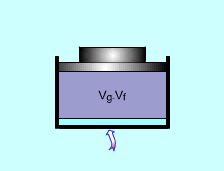| Ch 2. Pure Substances | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
| Phase |
Property Diagrams |
Property Tables |
Ideal Gas |
||||
| Property Diagrams | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
A piston-cylinder device is used to vaporize saturated liquid to saturated vapor under 100 kPa. The volume change and the amount of energy added need to be determined. Assumptions:
|
||
|
|
(1)Volume change The total volume of the saturated liquid Vf = vfm The total volume when all the water becomes saturated vapor. Vg = vgm The volume difference is: Vdifference = vgm - vfm = 10 (1.673 - 0.001) = 16.72 m3 (2) Amount of energy added Latent heat of vaporization of water under 100 kPa is LV = 2257.0 kJ/kg. It is the same amount of energy needed to change 1 kg saturated water to saturated vapor under 100 kPa. Q = m Lv = 10 (2257.0) = 22570 kJ |
|