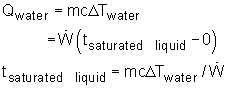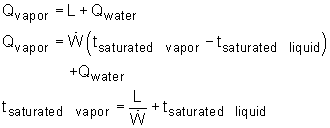| Ch 2. Pure Substances | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
| Phase |
Property Diagrams |
Property Tables |
Ideal Gas |
||||
| Phase and Phase Change | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
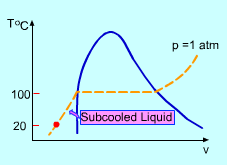
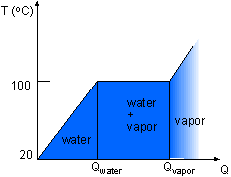
A student heats 1 kg of water of 20 oC in an experiment to learn the phase change of water. Temperature needs to be recorded for each phase. Assumptions:
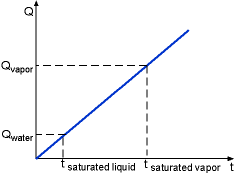
If the time when the water becomes saturated liquid and saturated vapor are known, then the recording time schedule can be determined. Qwater is the energy needed to heat the water from subcooled liquid (room temperature) to saturated liquid (saturated temperature). where Qvapor is the total energy needed to heat the room temperature water to saturated vapor. Using known values, ΔTwater = 100 - 20 = 80 oC tsaturated liquid = (1.0) (4.184) (80)/2.0 = 167.36 s tsaturated vapor = 2257.0/2.0 + 167.36 = 1295.86 s The time range for each phase is shown in the table. |
||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||