| Ch 10. Rankine Cycle | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
|
Rankine Cycle |
Reheat | Regeneration | Cogeneration | ||||
| Ideal Reheat Rankine Cycle | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
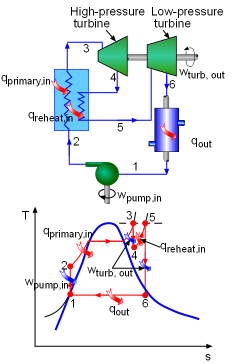
A reheat process is considered for a simple Rankine cycle to reduce the moisture content at the turbine exit. The pressure at which the steam should be reheated and the net work output are to be determined. Assumptions:
|
||
|
Saturated Water Temperature Table |
Model the cycle as an ideal reheat Rankine cycle. The schematic and the T-s diagram are shown on the left. (1) Determine the pressure at which the steam should be reheated The reheat pressure can be determined from the requirement that the entropies at state 5 and state 6 be the same. State 6 is saturated mixture with a pressure of 10 kPa. The requirement of the moisture content at state 6 gives that the quality of steam at state 6 is greater than 0.9. Thus, assume the quality of steam at state 6 equals to 0.9. Then the entropy at state 6 can be determined as following: x6 = 0.9 Since the steam will be reheated to the inlet temperature of the high-pressure turbine, and the entropies at state 5 and state 6 are the same, the pressure at state 5 can be determined from superheated vapor table. T5 = 600oC (given) Therefore, steam should be reheated at a pressure of 3.82 MPa to prevent a moisture content at the low-pressure turbine above 10.0 percent. (2) Determine the net work output after the addition of the reheat process To determine the net work output of the cycle, the enthalpies at all other states need to be obtained first. They can be found from water tables. State 1: Saturated liquid water State 3: Superheated vapor State
4: Superheated vapor State 5: Superheated vapor State 6: Saturated mixture |
|
The net work output of the cycle equals the difference between the turbines work and the pump work. wpump,in = v1 (P2 - P1) wturb,out = w turb,high + w turb,low Hence, the net work output of the cycle is wnet,out = wturb,out - wpump,in Heat input to the cycle equals the heat added by the primary heating process plus heat added in the reheat process. qin = qprimary + qreheat where h2 is determined from the energy balance of the pump. h2 =
h1 +
wpump,in Thus, the thermal efficiency of the cycle can be determined from ηth = wnet,out/qin = 1,731.8/3885.4 = 44.6% |
||
Note: the net work output, heat input and thermal efficiency of the cycle before adding the reheat process can be determined in a similar way using the simple ideal Rankine cycle model. wnet,out = 1448.2 kJ/kg This shows that the net work output, heat input, thermal efficiency are all increased after adding a reheat process. And the moisture content in the steam at the exit of the turbine is reduced from 19.0 percent to 10.0 percent. |
||