| Ch 6. Integrals | Multimedia Engineering Math | ||||||
|
Indefinite Integral |
Area |
Definite Integral |
Fundamental Theorem |
Substitution Rule |
|||
| Indefinite Integral | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Limits |
| 2. Derivatives I |
| 3. Derivatives II |
| 4. Mean Value |
| 5. Curve Sketching |
| 6. Integrals |
| 7. Inverse Functions |
| 8. Integration Tech. |
| 9. Integrate App. |
| 10. Parametric Eqs. |
| 11. Polar Coord. |
| 12. Series |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| |
||
| Introduction |
||
|
|
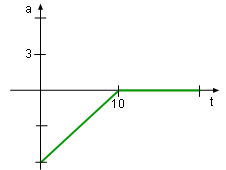
As raindrops fall, their surface enlarges which increases the resistance to accelerate. This acceleration can be modeled as where t is time. Assume the rain starts 800 meters above the ground and has an initial velocity of 10 m/s. |
|
| Questions |
||
| How long does it take the raindrop to reach the ground? | ||
| Approach |
||
|
|
|
|