| Ch 5. Rigid Body Equilibrium | Multimedia Engineering Statics | ||||||
|
2-D and 3-D Supports |
Equilibrium in 2-D |
Equilibrium in 3-D |
Indeterminate Objects | 2 and 3 Force Members | |||
| Equilibrium in 2-D | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Vectors |
| 3. Forces |
| 4. Moments |
| 5. Rigid Bodies |
| 6. Structures |
| 7. Centroids/Inertia |
| 8. Internal Loads |
| 9. Friction |
| 10. Work & Energy |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| STATICS - EXAMPLE |
||
| Example |
||
|
|
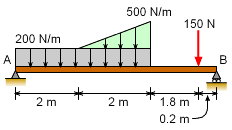
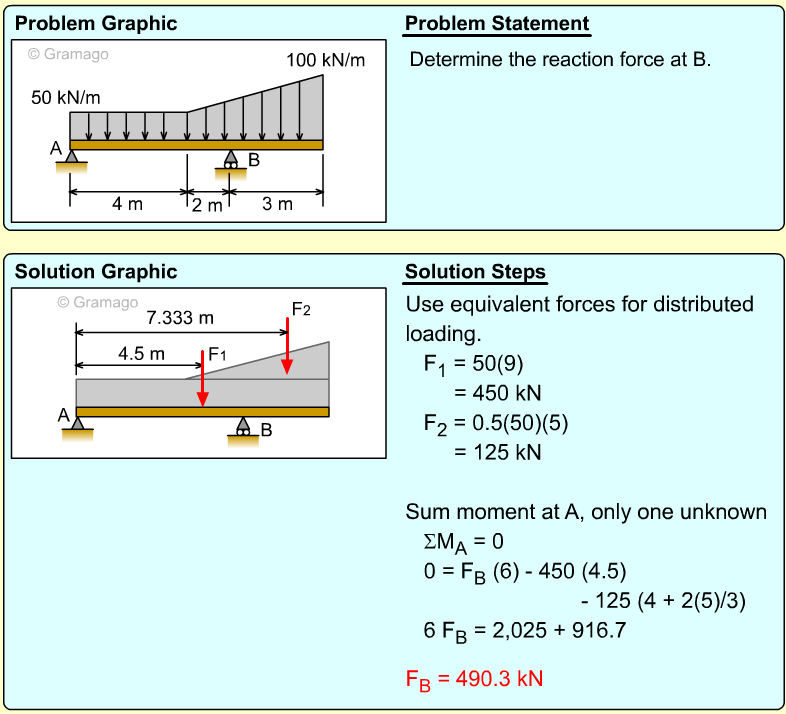
Calculate the reaction forces acting at A and B on the beam. |
|
| Solution |
||
|
|
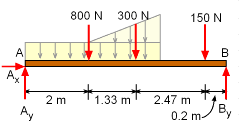
First convert the distributed loads into point loads and find their locations. For a rectangular uniform distributed load, the magnitude of the resultant force will be the product of the length of the rectangle and value of the distributed load. The location of the force resultant is always the center point (centroid) of the distributed load. The magnitude of the resultant force will be (200 N/m) (4 m) = 800 N and it will be at 2 m away from support A. For a triangular line load, the force resultant is one half of the peak value of the distributed load multiplied by the distance over which it acts. The location of the force resultant is two-thirds of the distance from the vertex to the peak value of the load. The magnitude of the resultant force will be (1/2) (2) (500 - 200) = 300 N and it is at 1.33 m from left vertex. The actual reactions can be found by applying equilibrium equations |
|
There will be three possible reactions at A and B namely Ax, Ay and By. which can be found by applying the equilibrium equations. ΣMA = 0 Equating forces give, ΣFy = 0 Since there is no horizontal applied load, Ax will be zero. | ||
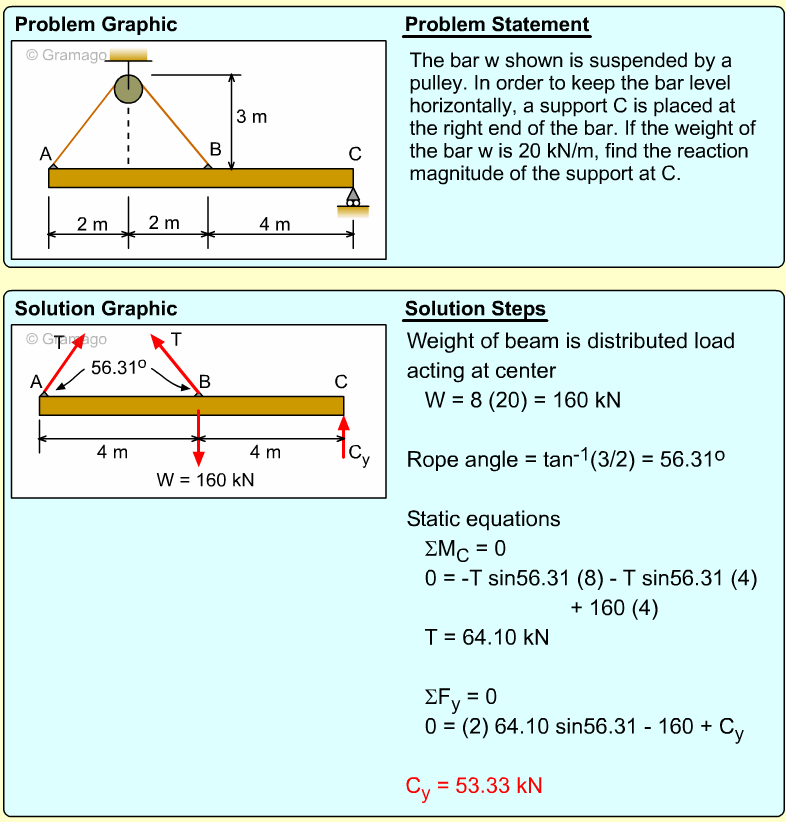
| Example Problem 1 |
||
|
||
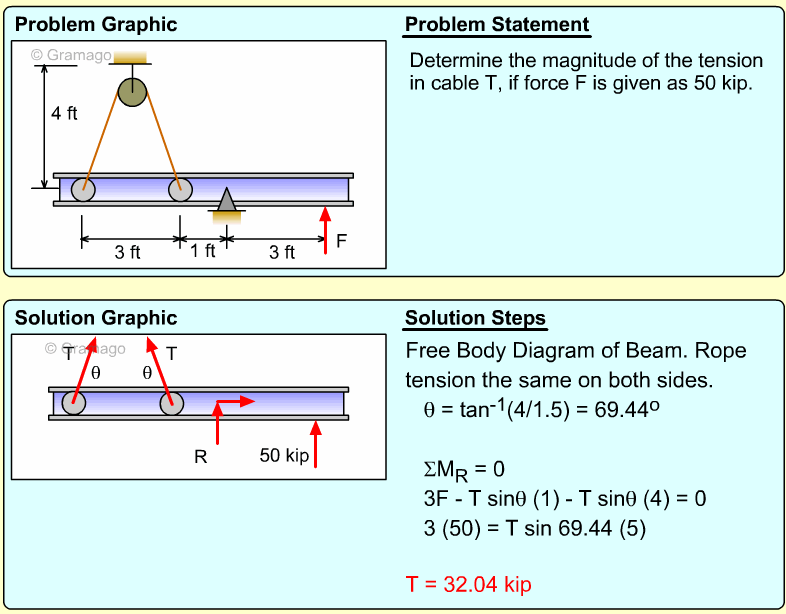
| Example Problem 2 |
||
|
||
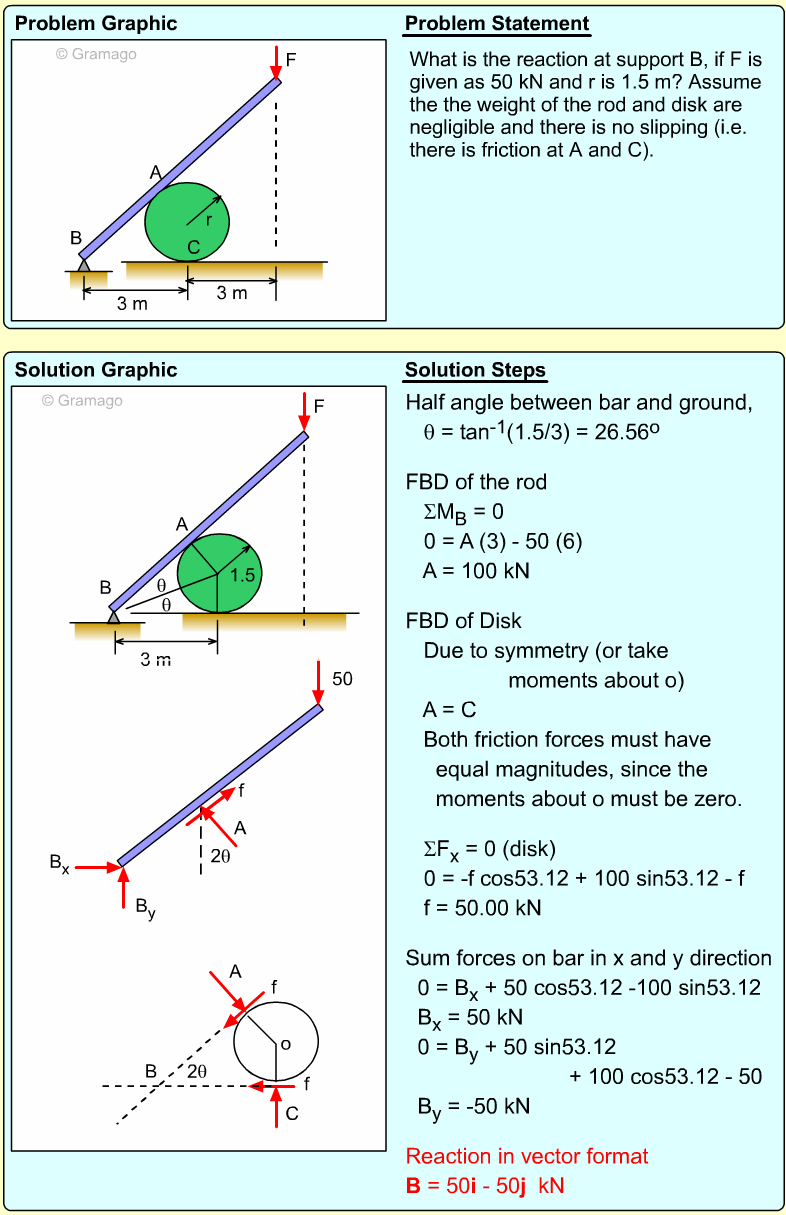
| Example Problem 3 |
||
|
||
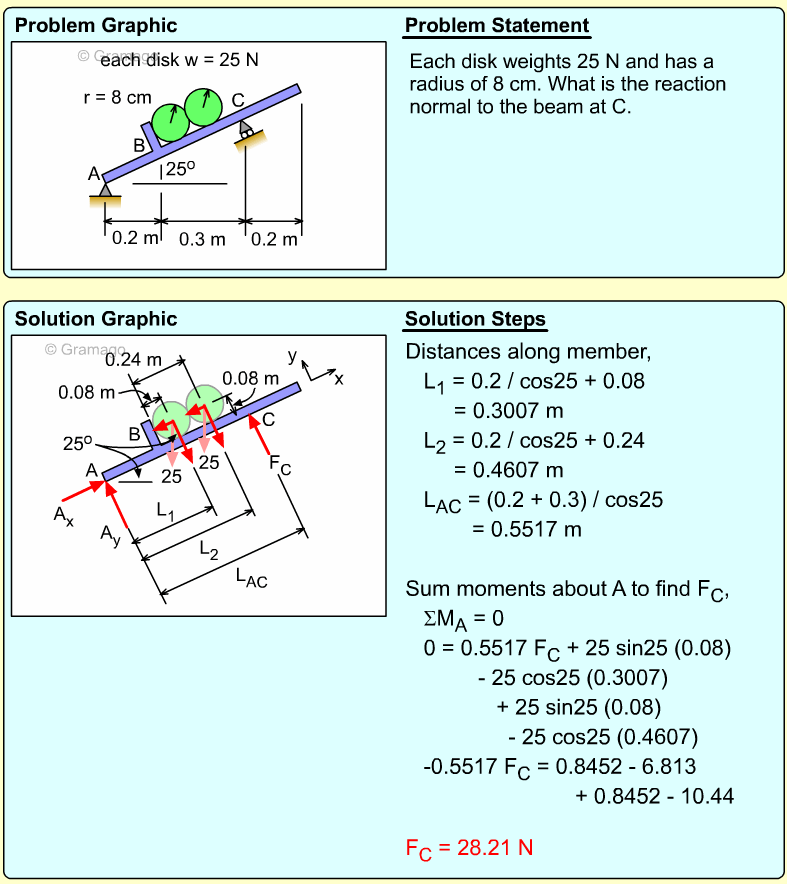
| Example Problem 4 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 5 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 6 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 7 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 8 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 9 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 10 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 11 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 12 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 13 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 14 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 15 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 16 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 17 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 18 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 19 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 20 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 21 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 22 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 23 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 24 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 25 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 26 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 27 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 28 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 29 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 30 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 31 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 32 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 33 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 34 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 35 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 36 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 37 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 38 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 39 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 40 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 41 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 42 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 43 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 44 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 45 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 46 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 47 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 48 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 49 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 50 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 51 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 52 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 53 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 54 |
||
|
||