| Ch 5. Rigid Body Equilibrium | Multimedia Engineering Statics | ||||||
|
2-D and 3-D Supports |
Equilibrium in 2-D |
Equilibrium in 3-D |
Indeterminate Objects | 2 and 3 Force Members | |||
| 2-D and 3-D Supports | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Vectors |
| 3. Forces |
| 4. Moments |
| 5. Rigid Bodies |
| 6. Structures |
| 7. Centroids/Inertia |
| 8. Internal Loads |
| 9. Friction |
| 10. Work & Energy |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
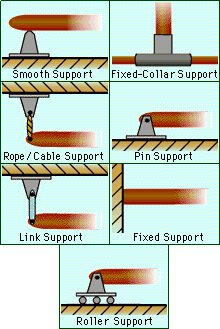 Basic 2D Boundary Conditions |
Before the equilibrium of rigid bodies can be investigated, the supports that hold them in place, or hold them to other objects, must be first analyzed. Supports that are commonly found in statics can be represented by stylized models called support conventions. An actual support may be a close approximation of a model. The forces and moments exerted on a rigid body by its supports are called reactions. These forces and moments are reacting to external loads that are applied to the rigid body. In general, if a support prevents translation in a given direction, then the support exerts a force in that direction. If rotation is prevented, then the support exerts a couple, or moment, in the direction of the rotation. Supports can be broken down into two categories: 2-D supports and 3-D supports. The table to the left shows common 2-D support conventions. To better understand the relationship between support conventions and support reactions, detailed explanation of three of the more commonly used support conventions are presented below. They are the pin support, the roller support, and the fixed support. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pin Support |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
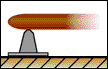
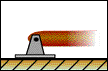
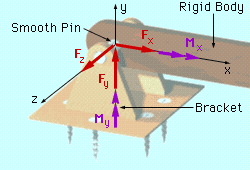 Pin Support |
With a pin support, a bracket and an object are connected by means of a smooth pin passing through the object and connected to the bracket. The pin prevents translation but permits rotation. Thus, the pin support exerts forces in any direction, but it cannot exert a moment about the axis of the pin. In 2-D, the reaction force of a pin can be broken down into two component forces parallel to the x and y axes. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Roller Support |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
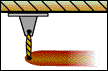
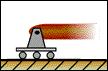
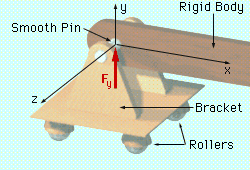 Roller Support |
The roller support is similar to a pin support but mounted on wheels. It cannot exert a couple about any axis, nor can it exert a force parallel to the surface on which the roller support rests. It can, however, exert a force perpendicular to the surface on which it rests. The roller permits rotation about any axis. It also permits translation in any direction parallel to the surface. It prohibits translation towards the surface. In 2-D, the reaction force of the roller support can be represented by one force perpendicular to the surface. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Support |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
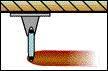
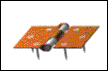
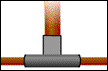
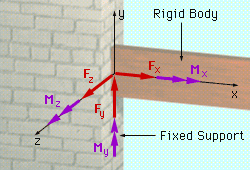 Fixed Support |
The fixed support prevents both translation and rotation about any axis. Thus, the fixed support prevents translation and rotation in any direction. In 2-D, the fixed support can be represented by component forces parallel to the x and y axes, and a couple that is perpendicular to the x-y plane. The table below includes a more comprehensive presentation of both 2D and 3D support conventions and their reactions. Click on any graphic to view a detailed animation of the support mechanism. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||