| Ch 5. Rigid Body Equilibrium | Multimedia Engineering Statics | ||||||
|
2-D and 3-D Supports |
Equilibrium in 2-D |
Equilibrium in 3-D |
Indeterminate Objects | 2 and 3 Force Members | |||
| 2-D and 3-D Supports | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Vectors |
| 3. Forces |
| 4. Moments |
| 5. Rigid Bodies |
| 6. Structures |
| 7. Centroids/Inertia |
| 8. Internal Loads |
| 9. Friction |
| 10. Work & Energy |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
 Coordinate System Diagram |
To simplify the analysis, determine the reactions that each support exerts on the trap door along each axis of a Cartesian coordinate system. Each reaction is assumed to be acting in the positive direction. | |
| Support 1 |
||
 Support 1: Sliding Hinge |
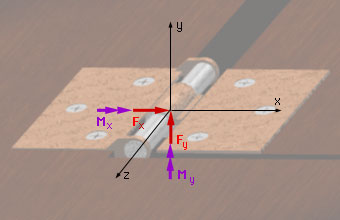
The first support appears to be a standard hinge at a quick glance. Upon further examination, it becomes clear that this support is actually a bearing with a circular shaft that can slide along the z-axis (standard hinges cannot). This type of support has two unknown reaction forces and two unknown reaction moments along the coordinate axes that are perpendicular to the axis of the bearing. There are, however, no reaction forces or moments along the axis of the bearing. Thus, the bearing can both translate and rotate along this axis. |
|
|
|
||
| Support 2 |
||
 Support 2: Standard Hinge |
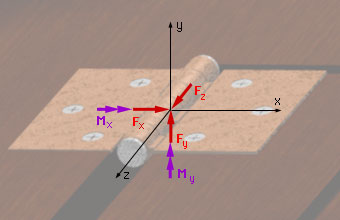
The second support is a standard hinge. A hinge has two unknown reaction forces and two unknown reaction moments along the coordinate axes that are perpendicular to the axis of the hinge. There is also a reaction force along the axis of the hinge (i.e. does not slide along the z-axis). There is, however, no reaction moment along the axis of the hinge. Thus, the hinge may only rotate about this axis. |
|
|
|
||
| Support 3 |
||
 Support 3: Bolt |
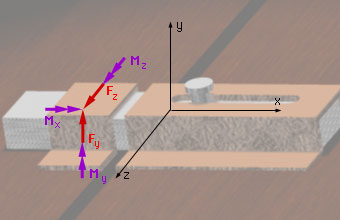
The third support is the bolt. This support does not permit any rotation around any axis. It has two unknown reaction forces and two unknown reaction moments along the coordinate axes that are perpendicular to the axis of the bearing. There is also a reaction moment along the axis of the bolt. Thus, the bolt only permits translation along the axis of the bolt. | |
|
|
||