| Ch 3. First Law of Thermodynamics | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
|
Conservation of Mass |
Conservation of Energy |
Solids and Liquids |
Ideal Gas | ||||
| Solids and Liquids | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
|
An elevator is designed to deliver books for the
bookshop located on the fourth floor of the library.
The
power required
to run the elevator when it is fully loaded and empty needs to be
determined. |
|
|
|
Assumptions:
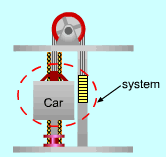
Consider the car and the counterweight as a system. It is a closed system because the car (with or without a load) and the counterweight are solids, hence the mass remains constant during the process. The energy balance for a closed system is: Q - W = (ΔU + ΔKE + ΔPE)system It can be simplified according to the following conditions:
The energy balance equation becomes: - W =(ΔPE)system |
|
|
|
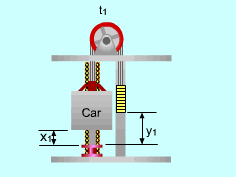
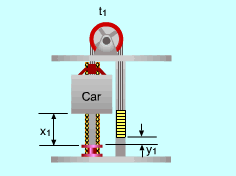
(1) Determine the power needed when the elevator is fully loaded and moving upwards From the analysis above, the work needed to run the fully loaded elevator upwards is: W = - (ΔPE)system The mass of the counterweight is: mcounter = (mcar + mload )(50%) At time t1, the total potential energy of the system is: (PE)1 = (mcar + mload )g x1 + mcounterg y1 At time t2, the total potential energy of the system changes to: (PE)2 =(mcar + mload )g x2 + mcounterg y2 (ΔPE)system =
(PE)2 - (PE)1 Since the ropes cannot be stretched, the distance that the car moves upwards is the same as the distance that the counterweight moves downwards. (x2 - x1) = - (y2 - y1) = (t2 - t1)v Hence, (ΔPE)system= (mcar + mload- mcounter)g (t2 - t1)v W = - (mcar + mload- mcounter)g (t2 - t1)v Power is work per unit time, and it is given by The negative sign means that work needs to be applied to the system
when the elevator runs upwards with full load. |
|
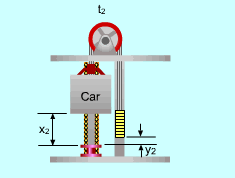
 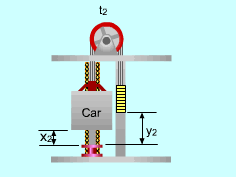 Locations of the Elevator at Time t1and t2 when the Elevator Moves Downwards |
(2) Determine the power needed when the elevator is empty and moving downwards At time t1, the total potential energy of the system is: (PE)1 = (mcar)g x1 + mcounterg y1 At time t2, the total potential energy of the system is: (PE)2 =(mcar)g x2 + mcounterg y2 (ΔPE)system =
(PE)2 - (PE)1 The counterweight moves upwards while the car moves downwards. y2 - y1 = - (x2 - x1) = (t2 - t1)v Hence, (ΔPE)system= (mcounter - mcar )g(t2 - t1)v Power can be determined by dividing the work by time. The result is negative which means that input power is required. (3) Determine the energy saved by using counterweight For a single delivery, the elevator runs upwards with full load and downwards with no load. Set mcounter equals to 0 in the above analysis. The energy needed for the elevator moving upwards and downwards are: The work is positive which means that no energy is needed to be applied to the system. The percent of energy saved by using the counterweight is (15,680 - 7,840 - 2,940)/15,680 = 31.3% |
|