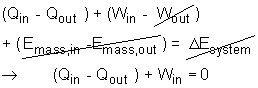| Ch 3. First Law of Thermodynamics | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
|
Conservation of Mass |
Conservation of Energy |
Solids and Liquids |
Ideal Gas | ||||
| Conservation of Energy | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
|
|
A window air conditioner is running to reduce the room temperature to the temperature setting. The operation time and the total heat released to the ambient need to be determined. Assumption: |
|
(1) Heat transferred to the air conditioner Qin In order to cool the room to the setting temperature, heat needs to be removed from the room, which is transferred to the air conditioner, and it is the energy entering the system. Qin = (50,000 J/oF) (90oF
- 75oF) |
||
(2) Total work input for the air conditioner Win According to the definition of COP, the amount of work input needed for the air conditioner is given by COP = Qin / Win Win = Qin / COP
= (750,000 J) / 2.5 The power input for the air conditioner is 900 W. So the operation time is: t = Win / This is a short time, and thus his room must be very small (maybe 10'x10'x7'). But then most student rooms are small. |
||
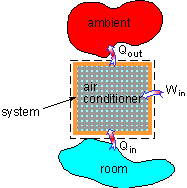 Energy Balance of the Air Conditioner |
(3) The total heat released to the ambient Qout The energy equation can be simplified according to the assumptions.
Qout = Qin + Win = 750,000 + 300,000
|
|