| Ch 2. Derivatives I | Multimedia Engineering Math | ||||||
|
Derivative Formulas |
Trigonometric Functions |
Differentiability |
Chain Rule |
Implicit Differentiation |
|||
| Derivative Formulas | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Limits |
| 2. Derivatives I |
| 3. Derivatives II |
| 4. Mean Value |
| 5. Curve Sketching |
| 6. Integrals |
| 7. Inverse Functions |
| 8. Integration Tech. |
| 9. Integrate App. |
| 10. Parametric Eqs. |
| 11. Polar Coord. |
| 12. Series |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| MATHEMATICS - CASE STUDY SOLUTION |
||
 Circular Ripple |
A football is kicked into a pool. It creates a circular
ripple that traveles outward with a speed of 2 ft/sec. How fast does
the circular area enlarge after 3 seconds? s = πr2 The enlarging circular area with respect to time t is s't or ds/dt ds/dt = d(πr2)/dt = d(π(r2))/dt = 2πr(dr/dt) When t = 3 seconds, r = (2)(3) = 6 So ds/dt = 2πr(dr/dt) = 2π(6)(2) = 24π ft2/sec |
|
| Discussion |
||
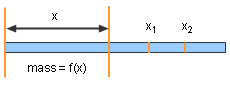 Non-homogeneous Linear Density Calculation |
In order to evaluate the rate of the enlarging circular area, the concept of derivative has been employed. Derivative is widely used in science and engineering research. For example, how to calculate the linear density of a non-homogeneous rod. The mass from the left end to the point x is mass = f(x) The mass between x2 and x1 is Δmass = f(x2) - f(x1) So the average density of the rod between x2 and x1 is average density = Δmass/Δx = ( f(x2) - f(x1))/(x2-x1) Letting x2 approaches x1, the linear density ρ of the rod at point x1 is the limit of the average density when Δx approaches 0. In other words, the linear density of the rod is the derivative of the mass with respect to length. Since the concept of derivative can apply to many problems in science and engineering, it is important for students to understand its physical meaning. |
|