| Ch 1. Stress and Strain | Multimedia Engineering Mechanics | ||||||
|
Normal Stress |
Shear and Bearing Stress |
Normal Strain |
Hooke's Law |
Thermal Effects |
Indeterminate Structures |
||
| Hooke's Law | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Stress/Strain |
| 2. Torsion |
| 3. Beam Shr/Moment |
| 4. Beam Stresses |
| 5. Beam Deflections |
| 6. Beam-Advanced |
| 7. Stress Analysis |
| 8. Strain Analysis |
| 9. Columns |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Mechanics Eqs |
| Sections |
| Material Properties |
| Structural Shapes |
| Beam Equations |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Example |
||
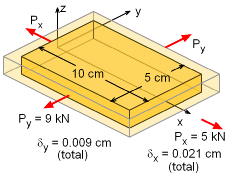 Plate with Applied Loads and Displacement |
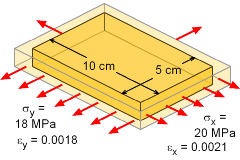
A 0.5 cm thick rectangular plate is pulled in tension by two loads in the x and y directions as shown. The total deflection in the x and y direction is 0.021 cm and 0.009 cm, respectively. What is the Poisson's ratio of the material? The z direction has no load and the deflection is not known. |
|
| Solution |
||
|
|
This problem involves loading from two directions, and thus requires at least the 2-D Hooke's Law. The 3-D Hooke's Law could be used, but since σz is zero, those equations will reduce to the 2-D equations. The equations are, εx = (σx - ν σy)/E The strains and stresses in the x and y direction need to be calculated. σx = Px/Ax = 5/[(0.05)(0.005)]
= 20 MPa εx = 0.021/10 = 0.0021 cm/cm Substituting the stresses and strains into the 2-D Hooke's Law equations, gives 0.0021 E = 20 - ν 18 Solving for ν gives, |
|
| Example Problem 1 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 2 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 3 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 4 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 5 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 6 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 7 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 8 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 9 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 10 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 11 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 12 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 13 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 14 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 15 |
||
|
||
| Example Problem 16 |
||
|
||