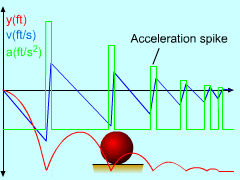
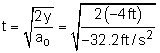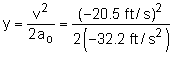| Ch 1. Particle General Motion | Multimedia Engineering Dynamics | ||||||
|
Position, Vel & Accel. |
Accel. vary w/ Time |
Accel. Constant | Rect. Coordinates | Norm/Tang. Coordinates | Polar Coordinates |
Relative Motion |
|
| Line Motion: Acceleration Constant | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| - Particle - |
| 1. General Motion |
| 2. Force & Accel. |
| 3. Energy |
| 4. Momentum |
| - Rigid Body - |
| 5. General Motion |
| 6. Force & Accel. |
| 7. Energy |
| 8. Momentum |
| 9. 3-D Motion |
| 10. Vibrations |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Dynamics Eqs |
| Sections |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||
| Solution of a) |
||
 Ball Diagram
|
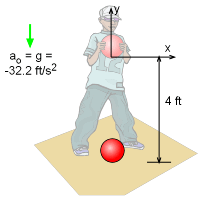
Begin by drawing a diagram of the ball at the moment it is released. The origin of the reference axis is fixed at the point where the ball is released, thus yo = 0 vo = 0 to = 0 y = -4 ft (final position when it hits the ground) ao = g = -32.2 ft/s2 To determine the velocity when the ball impacts the earth, the time it takes to travel the 4 ft first needs to be calculated. x(t) = xo + vo (t - to) + 1/2 ao (t - to)2 t = 0.498 s The time can now be substituted into the velocity equation, v = vo + ao (t - to) = (-32.2 ft/s2) (0.498 s) v = -16.0 ft/s = -10.9 mi/hr The negative represents the ball traveling downward in the negative y direction. |
|
| Solution of b) |
||
|
|
The third equation in the theory section can be used to determined height of the ball so that at impact it is traveling 14 mph. It is assumed that the ball velocity at release is zero. -14 mi/hr = -20.5 ft/s v2 = vo2
+ 2 ao (y - yo) This indicates that when released from rest, the ball will travel 6.55 ft in the negative y direction before its speed is 14 mph. Thus, the ball and the origin of the reference axis must be raised 6.55 ft above the ground. |
|