| Ch 1. Basics | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
| System |
Temperature & Pressure |
Heat and Work |
Energy | ||||
| Heat and Work | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| |
||
| Introduction |
||
|
|
Before ironing, an iron needs to be warmed up to a certain temperature. The iron temperature is different for different fabric. The resistance wires are used to generate the energy needed to warm the iron up. Known:
|
|
| Questions |
||
|
|
|
|
| Approach |
||
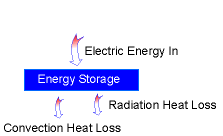 Energy Balance Diagram |
|
|