| Ch 1. Basics | Multimedia Engineering Thermodynamics | ||||||
| System |
Temperature & Pressure |
Heat and Work |
Energy | ||||
| Temperature and Pressure | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution |
| Chapter |
| 1. Basics |
| 2. Pure Substances |
| 3. First Law |
| 4. Energy Analysis |
| 5. Second Law |
| 6. Entropy |
| 7. Exergy Analysis |
| 8. Gas Power Cyc |
| 9. Brayton Cycle |
| 10. Rankine Cycle |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Thermo Tables |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
| |
||||||||||||||
| Units for Mass, Length, Time and Force |
||||||||||||||
| There are two widely used systems of units: the International System (or Systeme International d'Unites in French), S.I.; and the English System. The base units in the S.I. system are meters (m) for length, second (s) for time, and kilogram (kg) for mass. The force unit is derived using Newton's 2nd Law: F = ma = 1 kg (1 m/s2) = 1 kg m/s2 = 1 N The base units in the English system are foot (ft) for length, second (s) for time, and pound-force (lbf) for force. The mass unit is derived using Newton's 2nd Law: m = F/a = 1 lb/(ft/s2)
= 1 lb s2/ft The table to the left compares the two systems. All the units in thermodynamics can be derived from these base units. Details of the thermodynamic units will be introduced in the following sections. |
||||||||||||||
| Pressure |
||||||||||||||
 Definition of Pressure |
The absolute pressure (P) is the force
acting on unit area. In the SI system, the unit for pressure is Pa, Pascal.
In the English system, it is psi. Since Pa is a small unit in the SI system, other units are also used in thermodynamics, such as: 1 bar = 105Pa |
|||||||||||||
 Atmosphere |
The air surrounding the earth can be treated as a homogeneous gas, called atmosphere. Atmospheric pressure (Pa) is the pressure due to the force by the atmosphere mass. Standard atmospheric pressure is 101325 Pa. |
|||||||||||||
|
|
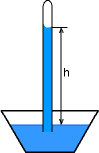
Barometer is a device used to measure the atmospheric pressure. Pa = ρ g h where |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
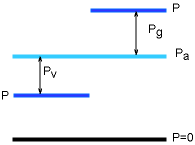
Gage Pressure and Vacuum Pressure |
Gage pressure (Pg) is the difference between the absolute pressure and the atmospheric pressure if the difference is positive. If the difference is negative, it is called vacuum pressure (Pv). Pg = P - Pa (P > Pa) Absolute pressure is used in thermodynamic relations and tables. |
|||||||||||||
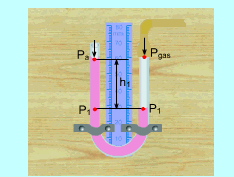 U-Tube Manometer |
U-Tube Manometer is used to measure pressure difference. One end of it is open to the atmosphere and the other end is connected to the equipment whose pressure is needed to be measured. At the right side, Usually, the second term on the right hand of the previous equation is negligible since the density of the work fluid is much larger than the density of the gas. P1 = Pgas At the left side, P1 = Pa + ρworking fluid g h1 Combine the two equations above, the pressure in the gas
tank can be determined as |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Temperature and the Zeroth Law |
||||||||||||||
|
|
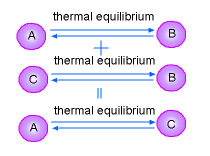
The measurement of the degree of hotness or coolness is temperature. If two bodies at different temperatures are brought together, the hot body will warm up the cold one. At the same time, the cold body will cool down the hot one. This process will end when the two bodies have the same temperatures. At that point, the two bodies are said to have reached thermal equilibrium. The Zeroth Law of thermodynamics states:
The Zeroth Law of thermodynamics is a basis for the validity
of temperature measurement. |
|||||||||||||
| Temperature Scales |
||||||||||||||
|
To establish a temperature scale, two fixed, easy duplicated points are used. The intermediate points are obtained by dividing the distance between into equal subdivisions of the scale length. |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
The relations between the above temperature
scales are:
T(R) = 1.8 T(K) |
||||||||||||||
|
Thermometers |
|||||||||||||
|
|
Thermometers measure temperature, by using materials that change in some way when they are heated or cooled. In a mercury or alcohol thermometer the liquid expands as it is heated and contracts when it is cooled, so the length of the liquid column becomes longer or shorter depending on the temperature. Modern thermometers are calibrated in standard temperature units such as Fahrenheit or Celsius. Three practical points for using thermometer are:
Digital thermometers almost replace the mercury ones
in nowadays because they are more accuracy and more easy to use. |
|||||||||||||