| Ch 1. Stress and Strain | Multimedia Engineering Mechanics | ||||||
|
Normal Stress |
Shear and Bearing Stress |
Normal Strain |
Hooke's Law |
Thermal Effects |
Indeterminate Structures |
||
| Normal Stress | Case Intro | Theory | Case Solution | Example |
| Chapter |
| 1. Stress/Strain |
| 2. Torsion |
| 3. Beam Shr/Moment |
| 4. Beam Stresses |
| 5. Beam Deflections |
| 6. Beam-Advanced |
| 7. Stress Analysis |
| 8. Strain Analysis |
| 9. Columns |
| Appendix |
| Basic Math |
| Units |
| Basic Mechanics Eqs |
| Sections |
| Material Properties |
| Structural Shapes |
| Beam Equations |
| eBooks |
| Dynamics |
| Fluids |
| Math |
| Mechanics |
| Statics |
| Thermodynamics |
| ©Kurt Gramoll |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
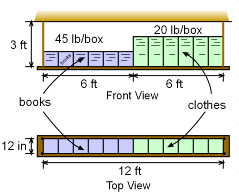
| Recall Dave, a college student, decided to construct a hanging shelf from the ceiling. He plans to place 12, 1-foot square boxes on the shelf. The left boxes will hold heavy books (45 lb each) and the right boxes will hold clothes (20 lb each). The shelf itself weighs 35 lb. Now, Dave needs to determine what size wood rods are needed to support the shelf and boxes. The rods come in increments of 1/16" and the wood will be Douglas Fir. First the actual load in each rod needs to be determined. A
free body diagram will help analyze the shelf and solve for the rod load.
Remember, there are two roads at each end. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
ΣFy =
0 Remember, the 2 before Ay and By is due to each end having two rods. ΣMA
= 0 Ay = 212.5 - 87.5 = 125 lb Thus, the two rods at A will each carry 125 lbs and the two rods at B will carry 87.5 lbs. Using the worse case, 125 lbs, the design load will be 4 times the actual load for the required factor of safety, P = 4(125) = 500 lb Using the
appendix, it is determined that Douglas Fir wood can withstand
a stress of 7,500 psi before it will fail. Using this failure stress, gives |
|||||||||||||||||
|
σ =
P/A The diameter of a cicular bar for 0.0667 in2 is π (D/2)2 =
A = 0.0667 in2 The smallest rod to be at least 0.2913 inches is 5/16" |
|||||||||||||||||
 Problem Diagram
Problem Diagram
